In Europe, many mobile network operators (MNOs) have completed or plan to switch off their legacy 2G or 3G networks.
These switch-offs are generally not regulated, but in nearly all cases commercially‑driven, allowing operators to:
- increase the spectrum available for new mobile technologies by re-farming 2G or 3G spectrum for the use of 4G and 5G; and
- generate network cost savings through lower network maintenance costs.
One of the reasons for the continued use of such legacy mobile networks is that they are still used, especially 2G networks, for machine-to-machine (M2M) services, such as smart meters and e-call systems.
Cullen International’s latest European benchmark shows that MNOs in 22 out of the 31 countries researched have completed or have plans to switch off their legacy 2G or 3G networks.
One MNO in Switzerland, Swisscom, switched off its 2G network in April 2021. MNOs' plans to switch off 2G networks exist in eight other European countries.
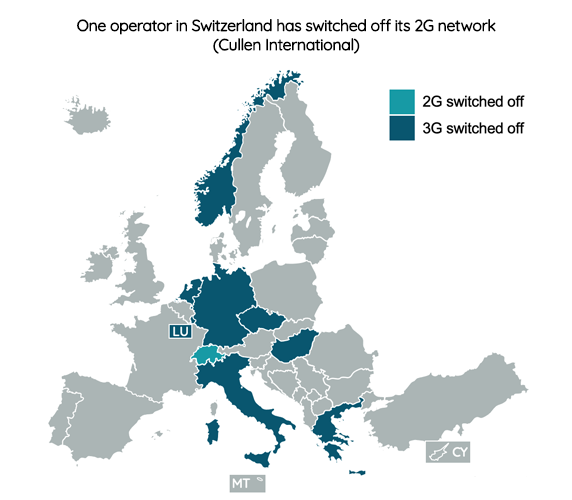
In only three countries, Czech Republic, Hungary and Italy, did the regulators become involved in whether 2G or 3G networks should be switched off.
Cullen International also has a similar benchmark on the 2G/3G switch-off in the MENA region.
To access the full benchmark, please click on “Access the full content” - or on “Request Access”, in case you are not subscribed to our European Telecoms Service.
more news
25 February 26
Protection of minors: overview of national initiatives on banning access to social media
Our latest benchmark shows that an increasing number of European countries are discussing a potential social media ban on children.
23 February 26
The DNA explained: universal service to serve the same goals under a revised approach
Cullen International is issuing a series of analyses on different aspects of the Digital Networks Act (DNA) proposal. This report covers universal service.
20 February 26
Revised Cybersecurity Act (CSA2) - Changes to the EU cybersecurity certification framework
Cullen International published an analysis of the proposed changes to the EU cybersecurity certification framework under the draft Cybersecurity Act 2 (CSA2) delivered by the European Commission on 20 January 2026.