Joint investments in European fibre broadband networks are made mainly by telecoms operators, with only limited involvement from utility companies or private equity funds. This is just one of the key findings from Cullen International’s new benchmark.
In Europe, the European Electronic Communications Code (EECC) aims to stimulate the deployment or upgrade of new FTTH or FTTB networks, especially in rural areas.
In the Commission's view, co-investment could mitigate some of the risks associated with investment in fibre networks, while at the same time preserving competition in fixed broadband networks.
Cullen International’s new European benchmark covers co-investment initiatives implemented before and after the entry into force of the EECC, showing the type of co-investment model adopted: joint-venture, reciprocal access or one-way access.
The research reveals the main co-investment initiatives for the rollout of FTTH/FTTB networks in 12 European countries: Belgium, Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Spain and Switzerland.
Only private initiatives are covered, excluding projects that are fully funded with public money and through public private partnerships.
Among the main findings of the benchmark are that:
- Most co-investment initiatives only involved telecoms operators. Utilities or private equity funds were involved in co-investments only in five countries.
- The joint-venture model is the type of co-investment model implemented in the majority of the researched countries.
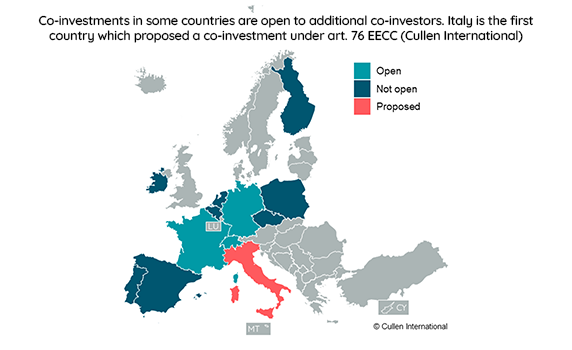
- Certain co-investments are open to additional potential co-investors in France, which mandates open co-investments in less densely populated areas, Germany and Switzerland. In Italy, a proposed offer provides for a seven-year timeline to agree to the co-investment.
To access the full benchmark, please click on “Access the full content” - or on “Request Access”, in case you are not subscribed to our European Telecoms Service.
more news
19 December 25
CSRD transposition: Belgium, Denmark, Finland and Slovenia transpose the “stop-the-clock” directive
Cullen International’s updated benchmark tracks the progress made by the 27 EU member states in transposing the CSRD and the related “stop-the-clock” directive.
19 December 25
Global trends in AI regulation
Our latest Global Trends benchmark compares policies and regulations on artificial intelligence (AI) across 14 jurisdictions around the world.
19 December 25
Implementation of European Media Freedom Act: general overview in 12 EU member states
Our new Media benchmark shows if there are initiatives/rules in the selected countries which aim to put into application the EU Media Freedom Act (EMFA). If yes, it describes the scope of the main measures proposed. The benchmark also provides information on the next legislative or regulatory steps.