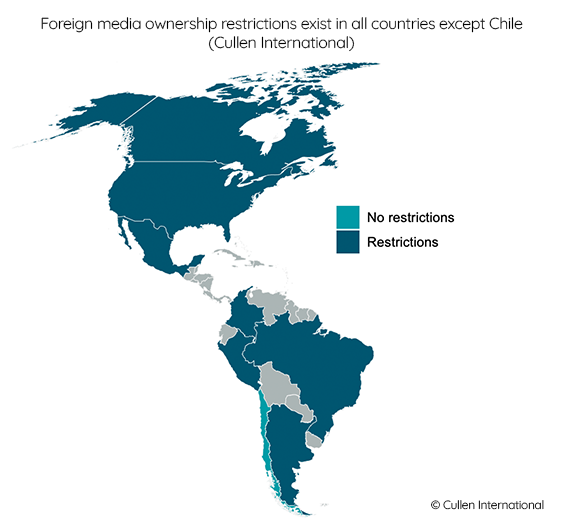
Most of the eight Americas countries covered in our benchmark on foreign ownership restrictions restrict the ownership of providers of audiovisual communications services. Only Chile among the countries studied has no law restricting foreign ownership of TV in any form. However, some legal requirements apply.
Argentina forbids foreign ownership of all forms of Argentinean audiovisual communication services, except for companies from countries that have reciprocity agreements.
Brazil has one of the toughest set of restrictions on the foreign ownership of free, over-the-air TV. Control of such a TV company is prohibited to foreigners or even to Brazilian citizens unless they have been naturalised for more than 10 years.
Canadian law explicitly provides that broadcasting, including entities involved in content production and distribution, must be "effectively owned and controlled by Canadians". The applicable ownership limits provide for a maximum of 20% of the shares in a broadcaster or 33.3% ownership of a holding company owning a broadcaster.
In the US, over-the-air broadcast licences can be granted to companies with more than 25% foreign ownership only with the prior approval of the national regulator.
For more information and to access the full benchmark, please click on “Access the full content” - or on “Request Access”, in case you are not subscribed to our Americas Media Service.
If you are also interested in the European context, please visit our benchmark on foreign ownership restrictions in Europe.
more news
04 March 26
The DNA explained: voluntary cooperation on IP interconnection, no network fees
Cullen International is issuing a series of analyses on different aspects of the Digital Networks Act (DNA) proposal. This report covers network contribution.
25 February 26
Protection of minors: overview of national initiatives on banning access to social media
Our latest benchmark shows that an increasing number of European countries are discussing a potential social media ban on children.
23 February 26
The DNA explained: universal service to serve the same goals under a revised approach
Cullen International is issuing a series of analyses on different aspects of the Digital Networks Act (DNA) proposal. This report covers universal service.